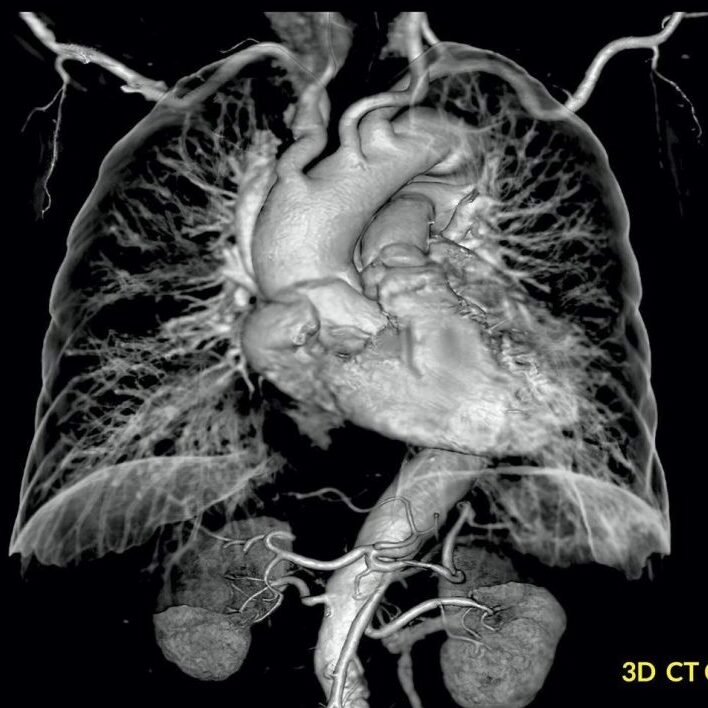
CT angiography, a sophisticated imaging technique, has become a cornerstone in the realm of vascular diagnostics. This non-invasive procedure combines the precision of computed tomography with contrast-enhanced imaging to offer a comprehensive visual exploration of blood vessels throughout the body. From detecting arterial blockages to assessing aneurysms, CT angiography stands as a powerful tool in unraveling the intricacies of vascular health.
How CT Angiography Works:
CT angiography involves the injection of a contrast dye into the bloodstream, enhancing the visibility of blood vessels during imaging. As the dye courses through the vascular system, a series of X-ray images are captured. These images are then reconstructed into detailed, cross-sectional views, providing healthcare professionals with a dynamic and three-dimensional portrayal of the patient’s vascular anatomy.
Diagnostic Applications:
- Coronary Artery Evaluation: CT angiography is widely employed for assessing coronary arteries, aiding in the detection of arterial blockages or stenosis. This information is crucial for cardiologists in evaluating cardiac health and determining appropriate interventions.
- Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Diagnosis: In cases of suspected peripheral arterial disease, CT angiography is instrumental in visualizing blood flow to the extremities. It helps identify blockages or narrowing in the arteries, guiding treatment decisions for conditions such as leg pain or claudication.
- Aneurysm Detection: The technique excels in identifying aneurysms, abnormal bulges in blood vessels that pose a risk of rupture. CT angiography provides detailed insights into the size, shape, and location of aneurysms, supporting timely intervention.
- Pulmonary Embolism Assessment: CT angiography is a primary diagnostic tool for evaluating pulmonary embolisms. By visualizing blood flow within the pulmonary arteries, healthcare professionals can swiftly identify obstructions and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
Patient Benefits:
CT angiography offers several advantages to patients, including its non-invasive nature, rapid imaging acquisition, and reduced exposure to radiation due to evolving low-dose protocols. Patients experience minimal discomfort during the procedure, making it a preferred choice for vascular assessments.
Conclusion:
In the dynamic landscape of vascular diagnostics, CT angiography stands as a pivotal player, offering a detailed roadmap of blood vessels without the need for invasive procedures. From coronary health to peripheral vascular assessments, this imaging modality empowers healthcare professionals with the information needed for precise diagnoses and targeted interventions, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes in the realm of vascular health.