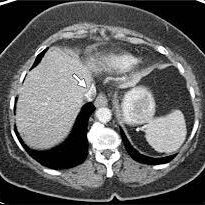
The CT scan of the Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) marks a significant advancement in vascular imaging, providing detailed insights into the anatomy and function of this crucial blood vessel. This specialized imaging modality utilizes computed tomography to capture high-resolution images of the IVC, offering healthcare professionals a comprehensive understanding of its structure and potential abnormalities. Let’s explore how CT scans of the IVC are enhancing diagnostic capabilities and contributing to the management of vascular health.
Detailed Imaging Overview:
CT scans of the Inferior Vena Cava focus on capturing detailed cross-sectional images of this large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium of the heart. The imaging modality employs advanced technology to visualize the IVC’s size, shape, and any potential abnormalities along its course.
Diagnostic Applications:
- Assessment of Vascular Anatomy: CT scans of the IVC provide detailed information about the vascular anatomy, including the size and course of the vein. This is essential for understanding the normal configuration and identifying any variations or anomalies.
- Detection of Thrombus or Blood Clots: The imaging modality is instrumental in detecting the presence of blood clots or thrombi within the IVC. Accurate visualization of these abnormalities is crucial for diagnosis and informs the appropriate course of treatment.
- Evaluation of IVC Filter Placement: In cases where an IVC filter is placed to prevent blood clots from traveling to the lungs, CT scans assist in evaluating the position and integrity of the filter. This is essential for ensuring the effectiveness of the filter and identifying any complications.
- Identification of Vascular Compression or Obstruction: CT scans help identify conditions leading to compression or obstruction of the IVC. This includes tumors, enlarged lymph nodes, or other structures that may impact blood flow within the vessel.
Patient-Centric Advantages:
CT scans of the IVC prioritize patient-centric advantages by offering a non-invasive and efficient means of vascular imaging. The procedure is typically quick, and advancements in technology have led to the use of lower radiation doses, ensuring patient safety without compromising the diagnostic quality of the images.
Conclusion:
CT scans of the Inferior Vena Cava have emerged as indispensable tools in vascular diagnostics, providing healthcare professionals with a comprehensive visual map of this vital blood vessel. From assessing vascular anatomy to detecting thrombi and evaluating filter placement, this imaging modality plays a pivotal role in shaping accurate diagnoses and guiding tailored treatment strategies for patients with IVC-related concerns.