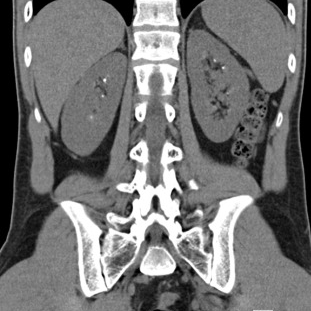
CT of KUB (Kidneys, Ureters, and Bladder) is a specialized imaging technique that plays a crucial role in examining the urinary tract and adjacent structures. This advanced diagnostic tool utilizes computed tomography to provide detailed and cross-sectional views of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and surrounding areas. CT of KUB stands as a valuable resource for healthcare professionals in diagnosing a range of urinary system conditions with precision.
Visualizing Renal Anatomy:
CT of KUB offers a comprehensive visual examination of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder, capturing high-resolution images of the internal structures. This imaging modality allows healthcare professionals to assess the size, shape, and condition of the kidneys, identify obstructions, and detect abnormalities within the urinary tract.
Diagnostic Applications:
- Renal Calculi (Kidney Stones) Detection: CT of KUB excels in identifying and characterizing renal calculi, commonly known as kidney stones. The detailed imaging provides information about the size, location, and composition of stones, facilitating appropriate treatment decisions.
- Evaluation of Renal Masses and Tumors: This imaging technique is instrumental in visualizing and characterizing renal masses and tumors. CT of KUB helps differentiate between benign and malignant lesions, guiding healthcare professionals in formulating effective treatment plans.
- Ureteral and Bladder Abnormalities: Beyond the kidneys, CT of KUB allows for the detection of abnormalities in the ureters and bladder. This includes identifying strictures, tumors, or congenital anomalies, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various urinary tract conditions.
- Assessment of Hematuria: In cases of unexplained blood in the urine (hematuria), CT of KUB helps identify the source of bleeding within the urinary system. It provides a thorough examination, assisting in the diagnosis of conditions contributing to hematuria.
Patient-Centric Features:
CT of KUB prioritizes patient comfort and safety by utilizing low-dose radiation protocols. This ensures that patients receive high-quality diagnostic images while minimizing potential risks associated with radiation exposure. The procedure is generally quick, enhancing the overall patient experience.
Conclusion:
CT of KUB stands as a vital diagnostic tool in the assessment of renal and urinary system health. By offering detailed views of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder, this imaging modality empowers healthcare professionals to make accurate diagnoses, guide appropriate treatments, and contribute to improved outcomes for patients experiencing urinary system concerns.