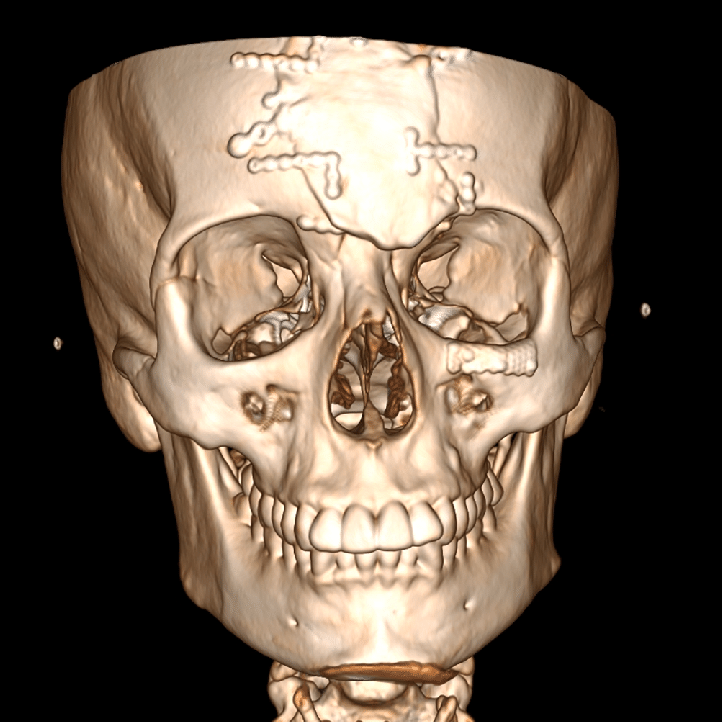
In the realm of medical imaging, the advent of 3D CT scans has introduced a transformative approach to visualizing and understanding the intricate structures of the face. This advanced imaging technique goes beyond traditional two-dimensional imaging, providing healthcare professionals with a three-dimensional perspective of facial anatomy. Let’s delve into the groundbreaking world of 3D CT scans for the face and explore how this technology is revolutionizing diagnostics.
Revolutionizing Facial Imaging:
3D CT scans of the face employ computed tomography technology to generate detailed, three-dimensional representations of the facial structures. This includes bones, soft tissues, sinuses, and intricate details of facial features. The result is a comprehensive visual dataset that allows for a more thorough assessment compared to traditional imaging methods.
Diagnostic Applications:
- Facial Fractures and Trauma: 3D CT scans are instrumental in assessing facial fractures and trauma. The three-dimensional visualization enables healthcare professionals to precisely identify the location, extent, and alignment of facial fractures, facilitating accurate treatment planning.
- Maxillofacial Surgery Planning: Surgeons benefit significantly from 3D CT scans when planning maxillofacial surgeries. The detailed imaging assists in understanding the spatial relationships between facial structures, guiding surgical interventions for procedures such as reconstructive surgery or orthognathic surgery.
- Dental and Orthodontic Assessments: Dentists and orthodontists utilize 3D CT scans to assess dental and jaw structures with unprecedented clarity. This technology aids in the diagnosis of dental conditions, evaluating tooth positioning, jaw alignment, and the presence of anomalies such as impacted teeth.
- Sinus and Nasal Evaluations: 3D CT scans provide a comprehensive view of the sinuses and nasal structures. This is particularly valuable for diagnosing sinusitis, nasal polyps, or anatomical variations that may contribute to respiratory issues.
Patient-Centric Advantages:
Beyond its diagnostic prowess, 3D CT scans for the face prioritize patient-centric advantages. The technology minimizes the need for multiple imaging sessions, streamlining the diagnostic process. Additionally, it enhances patient understanding by providing clear visualizations that can aid in discussions about treatment options and surgical procedures.
Conclusion:
The integration of 3D CT scans into facial imaging represents a paradigm shift in diagnostic precision. By offering detailed three-dimensional reconstructions, this technology empowers healthcare professionals with unparalleled insights into facial anatomy and pathology. From trauma assessments to surgical planning and dental evaluations, 3D CT scans for the face are reshaping the landscape of facial diagnostics, promising more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment strategies for patients.