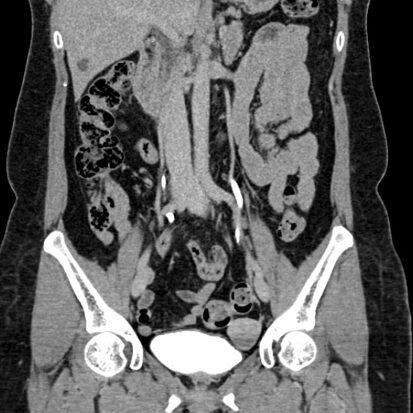
CT urography, a specialized imaging technique, has emerged as a valuable tool in the comprehensive assessment of the urinary system. This diagnostic procedure combines the precision of computed tomography with contrast-enhanced imaging to provide detailed insights into the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and surrounding structures. Offering a non-invasive and thorough examination, CT urography plays a crucial role in diagnosing various urinary tract conditions and guiding appropriate treatment plans.
How CT Urography Works:
CT urography involves the use of contrast dye, which is injected into the bloodstream to enhance the visibility of the urinary tract during imaging. As the dye circulates through the kidneys and urinary system, detailed cross-sectional images are captured. These images are then reconstructed, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize the anatomy and identify abnormalities.
Diagnostic Applications:
- Renal Stone Detection: CT urography is highly effective in identifying and characterizing renal stones. The detailed imaging allows for accurate assessment of stone size, location, and potential obstructions, aiding in treatment decisions.
- Evaluation of Kidney Tumors: The technique is instrumental in visualizing kidney tumors and assessing their characteristics. CT urography helps healthcare professionals differentiate between benign and malignant lesions, guiding decisions on further management.
- Ureteral and Bladder Abnormalities: By providing clear images of the ureters and bladder, CT urography facilitates the detection of abnormalities such as strictures, tumors, or congenital anomalies. This is crucial for diagnosing and planning appropriate interventions.
- Assessment of Hematuria: In cases of unexplained blood in the urine (hematuria), CT urography helps identify the source of bleeding. It provides a comprehensive view of the urinary tract, assisting in the diagnosis of conditions contributing to hematuria.
Patient Benefits:
CT urography offers several advantages to patients, including its non-invasive nature, rapid image acquisition, and the ability to visualize the entire urinary system in a single examination. The procedure is well-tolerated, and the use of low-dose radiation protocols contributes to patient safety.
Conclusion:
In the realm of urinary health diagnostics, CT urography stands as a powerful and versatile tool. Its ability to provide detailed images of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder enables healthcare professionals to make accurate diagnoses and formulate targeted treatment plans. With its non-invasive nature and comprehensive imaging capabilities, CT urography continues to play a pivotal role in enhancing the understanding and management of various urinary tract conditions.