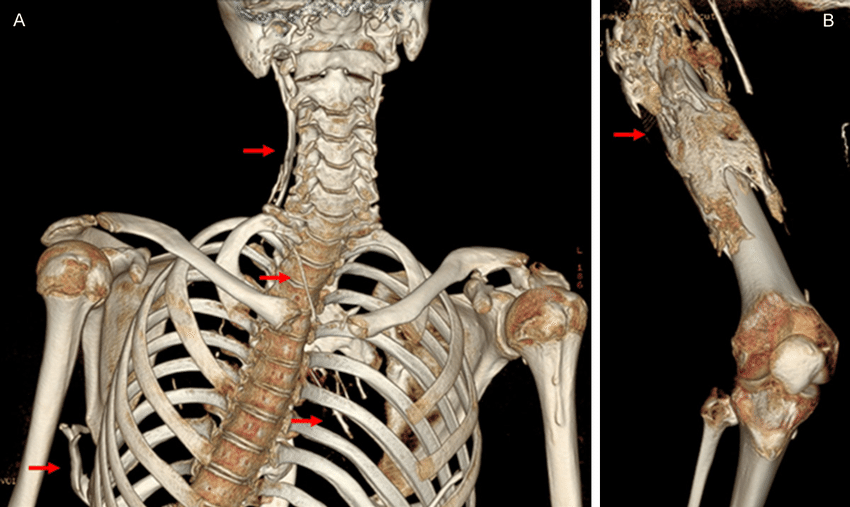
Three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction in computed tomography (CT) imaging provides several advantages, enhancing the visualization and interpretation of anatomical structures. Here are some advantages of 3D reconstruction in CT:
- Spatial Visualization:
- Enhanced Understanding: 3D reconstruction provides a more intuitive and realistic spatial representation of anatomical structures compared to traditional two-dimensional images. It allows healthcare professionals to better understand the spatial relationships between organs, vessels, and other structures.
- Surgical Planning:
- Precision in Surgical Procedures: 3D reconstructions are valuable for surgical planning, especially in complex cases. Surgeons can use the 3D images to visualize the anatomy, plan the approach, and determine the optimal trajectory for procedures, leading to increased precision during surgery.
- Education and Communication:
- Effective Communication: 3D reconstructions serve as powerful tools for communicating complex anatomical information to patients, medical students, and other healthcare professionals. They facilitate better understanding and communication of pathology, treatment plans, and outcomes.
- Orthopedic Assessments:
- Fracture Evaluation: In orthopedics, 3D reconstructions are beneficial for assessing fractures, joint surfaces, and alignment. They provide a comprehensive view of complex bone structures, aiding in the planning of orthopedic surgeries and fracture reduction.
- Dental and Maxillofacial Applications:
- Implant Planning: In dentistry and maxillofacial surgery, 3D reconstructions are used for implant planning. Dentists and oral surgeons can visualize the jawbone, teeth, and surrounding structures in three dimensions, aiding in precise implant placement.
- Cardiac Imaging:
- Visualization of Cardiac Anatomy: 3D reconstructions are particularly useful in cardiac imaging. They allow for detailed visualization of the heart, its chambers, valves, and blood vessels, assisting in the assessment of cardiac anatomy and function.
- Vascular Studies:
- Vascular Anatomy: 3D reconstructions are applied in vascular studies, providing a clear depiction of blood vessels, their branching patterns, and potential abnormalities. This is valuable for preoperative planning in vascular surgery and interventional procedures.
- Oncological Imaging:
- Tumor Localization: In oncology, 3D reconstructions assist in localizing tumors within complex anatomical structures. This aids in treatment planning, radiation therapy, and the assessment of tumor relationships with adjacent organs.
- Trauma Evaluation:
- Visualization of Traumatic Injuries: 3D reconstructions contribute to the visualization and assessment of traumatic injuries, such as fractures and dislocations. This is crucial for evaluating the extent of trauma and planning appropriate interventions.
- Research and Scientific Visualization:
- Scientific Exploration: 3D reconstructions are valuable tools in medical research for exploring anatomical variations, studying disease processes, and enhancing our understanding of complex physiological systems.
It’s important to note that while 3D reconstruction provides valuable information, it should be used judiciously, considering factors such as radiation exposure (in the case of CT scans), the clinical context, and the specific needs of the patient. The advantages of 3D reconstruction contribute to improved diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and overall patient care in various medical specialties.