CT (computed tomography) imaging is a crucial tool in the assessment of trauma patients, providing detailed cross-sectional images that help diagnose injuries, guide treatment decisions, and inform surgical interventions. CT is often employed in trauma situations due to its speed, accuracy, and ability to capture images of various structures in the body simultaneously. Here are key aspects of the role of CT in trauma:
- Trauma Protocols:
- Hospitals often have trauma protocols that include the rapid use of CT scans in the initial evaluation of trauma patients. This is especially true for cases of significant trauma, such as motor vehicle accidents or falls from height.
- Head and Brain Injuries:
- CT scans of the head are commonly performed to assess for traumatic brain injuries, including fractures, hemorrhages, contusions, and swelling.
- Cervical Spine Injuries:
- CT scans of the cervical spine are used to evaluate for fractures or dislocations in patients with suspected neck injuries.
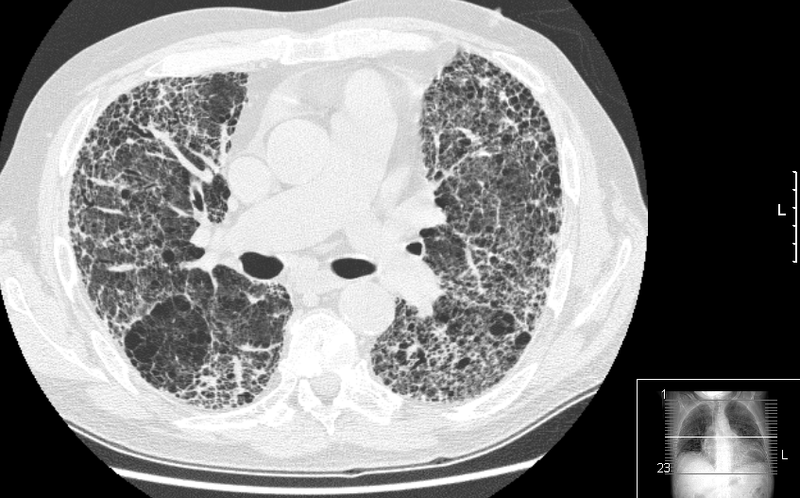
- Chest Injuries:
- CT imaging of the chest helps identify injuries to the lungs, ribs, and other thoracic structures. It is valuable for detecting pneumothorax, hemothorax, and rib fractures.
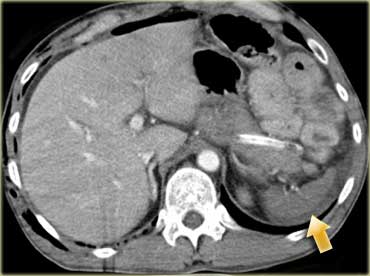
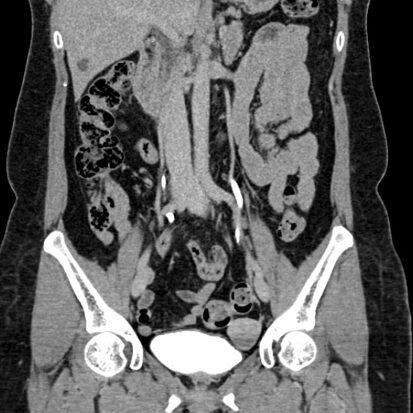
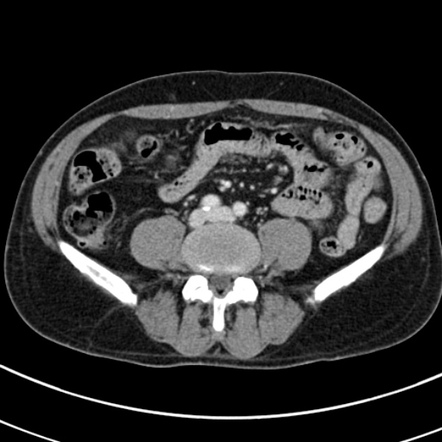
- Abdominal Injuries:
- CT scans of the abdomen and pelvis are crucial for evaluating injuries to abdominal organs (e.g., liver, spleen, kidneys), detecting intra-abdominal bleeding, and assessing for pelvic fractures.
- Pelvic Injuries:
- CT is used to assess for fractures and other injuries to the pelvic bones, which are common in trauma situations.
- Spinal Injuries:
- Beyond the cervical spine, CT can be employed to evaluate other regions of the spine for fractures or dislocations.
- Extremity Injuries:
- While X-rays are often used for initial assessments of extremity injuries, CT may be utilized to provide more detailed information about complex fractures or joint injuries.
- Whole-Body Trauma CT:
- Some trauma centers use whole-body trauma CT protocols, where a single scan captures images of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis in one examination.
- Vascular Injuries:
- CT angiography (CTA) may be employed to assess for vascular injuries, such as arterial or venous tears, especially in the setting of penetrating trauma.
- Rapid Imaging:
- CT is known for its speed, allowing for rapid imaging and quick assessment of critical injuries in trauma patients.
The use of CT in trauma situations is guided by the principles of the Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) protocol, which emphasizes the rapid and systematic evaluation of trauma patients. The information obtained from CT scans helps guide treatment decisions, surgical interventions, and ongoing management in collaboration with other diagnostic tools and clinical evaluations.