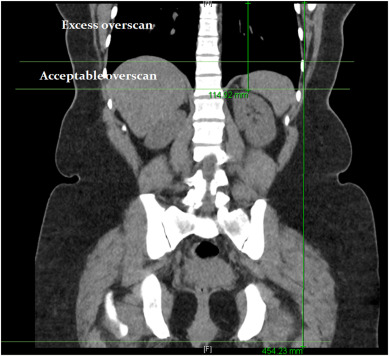
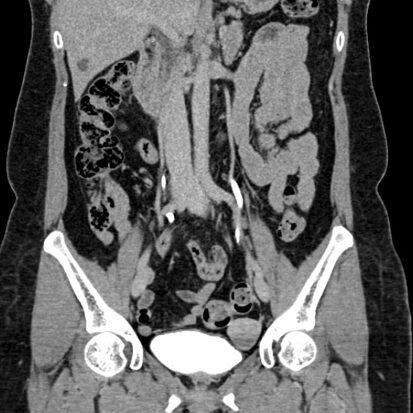
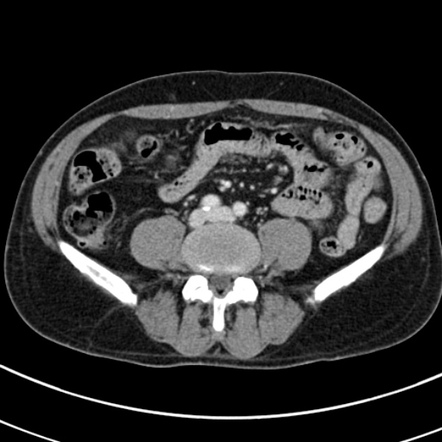
Application of artificial intelligence (AI) in CT scans of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder (KUB). CT KUB is a diagnostic imaging technique used to visualize these structures for various medical purposes, such as detecting kidney stones, assessing urinary tract abnormalities, or investigating causes of abdominal pain.
Here’s how AI may be applied in the context of CT KUB:
- Image Analysis:
- Automated Detection: AI algorithms can be trained to automatically detect and analyze structures within CT images, such as identifying kidney stones, measuring organ dimensions, or highlighting abnormalities.
- Diagnostic Support:
- Pattern Recognition: AI systems can be trained to recognize patterns associated with different conditions, aiding radiologists in diagnosing kidney and urinary tract disorders more efficiently.
- Workflow Optimization:
- Prioritization: AI can assist in prioritizing cases based on urgency, helping healthcare professionals focus on critical cases more quickly.
- Quantitative Measurements:
- Volume and Density Calculations: AI algorithms can perform quantitative measurements, such as calculating stone size, which can be valuable for treatment planning.
- Quality Assurance:
- Image Quality Assessment: AI can contribute to ensuring the quality of CT images, helping identify any issues that may impact diagnostic accuracy.
- Speed and Efficiency:
- Faster Analysis: AI-powered tools can process and analyze CT images rapidly, potentially reducing the time needed for radiologists to interpret results.
- Research and Data Analysis:
- Population Health Studies: AI can assist in analyzing large datasets derived from CT scans, contributing to research efforts and population health studies related to kidney and urinary tract conditions.
It’s important to note that while AI has the potential to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of medical imaging interpretation, it is not a replacement for the expertise of healthcare professionals. AI applications in medical imaging are developed to support and augment the work of radiologists and clinicians, providing them with additional tools to make more informed diagnoses and treatment decisions.