CT (computed tomography) of the abdomen is a commonly used imaging modality for the diagnosis of appendicitis, an inflammatory condition of the appendix. Appendicitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Here’s how CT abdomen plays a crucial role in the evaluation of appendicitis:
Indications for CT Abdomen in Appendicitis:
- Diagnostic Confirmation:
- CT is often used to confirm or rule out the diagnosis of appendicitis when there is clinical suspicion based on symptoms and physical examination.
- Uncertain Clinical Presentation:
- In cases where the clinical presentation is atypical or the diagnosis is uncertain, CT can provide valuable information.
- Evaluation of Complications:
- CT helps assess the severity of appendicitis and identify complications such as perforation, abscess formation, or localized peritonitis.
- Differential Diagnosis:
- CT is useful for distinguishing appendicitis from other causes of abdominal pain that may have similar symptoms.
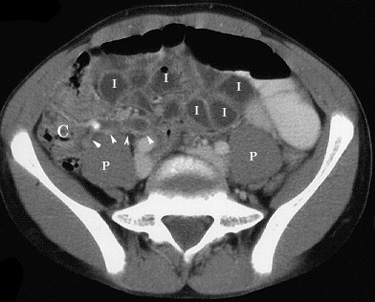
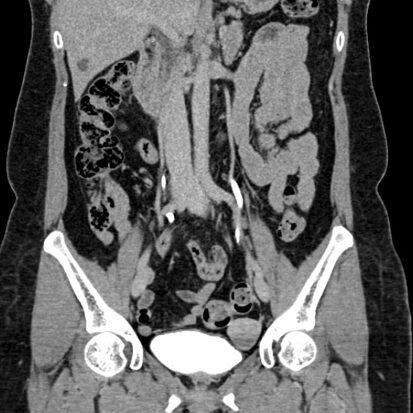
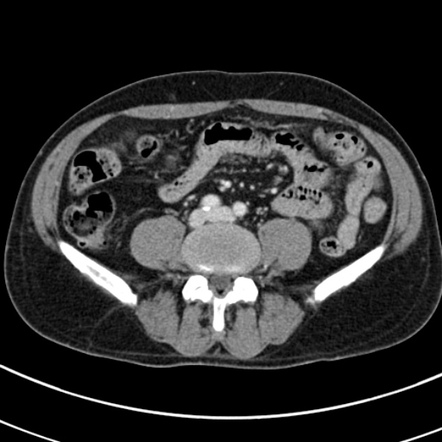
Key Findings on CT in Appendicitis:
- Enlarged Appendix:
- CT can identify an enlarged and inflamed appendix, a key characteristic of appendicitis.
- Periappendiceal Fat Stranding:
- Inflammation of the appendix can cause fat stranding, which is visible on CT as increased density or haziness around the appendix.
- Appendiceal Wall Thickening:
- CT can reveal thickening of the appendix wall, another sign of inflammation.
- Periappendiceal Fluid:
- In cases of appendicitis, fluid accumulation around the appendix (periappendiceal fluid) may be seen on CT.
- Abscess Formation:
- CT helps identify the presence of abscesses or localized collections of pus, which may occur in complicated cases.
- Free Air (Perforation):
- If the appendix perforates, leading to the release of air into the abdominal cavity, CT can detect the presence of free air.
Procedure:
- Contrast Administration:
- In many cases, a contrast dye is administered intravenously to enhance the visibility of structures in the abdomen.
- Imaging Acquisition:
- The patient lies on a table that moves through the CT scanner. Multiple X-ray images are taken, and a computer processes the data to create detailed cross-sectional images.
- Interpretation:
- The images are interpreted by a radiologist, who assesses the size, appearance, and condition of the appendix and surrounding structures.
CT abdomen is considered a sensitive and specific imaging modality for diagnosing appendicitis, and its use can help guide appropriate and timely treatment decisions. However, the decision to perform a CT scan is made based on the patient’s clinical presentation, and not all cases of suspected appendicitis may require imaging. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate diagnostic approach.