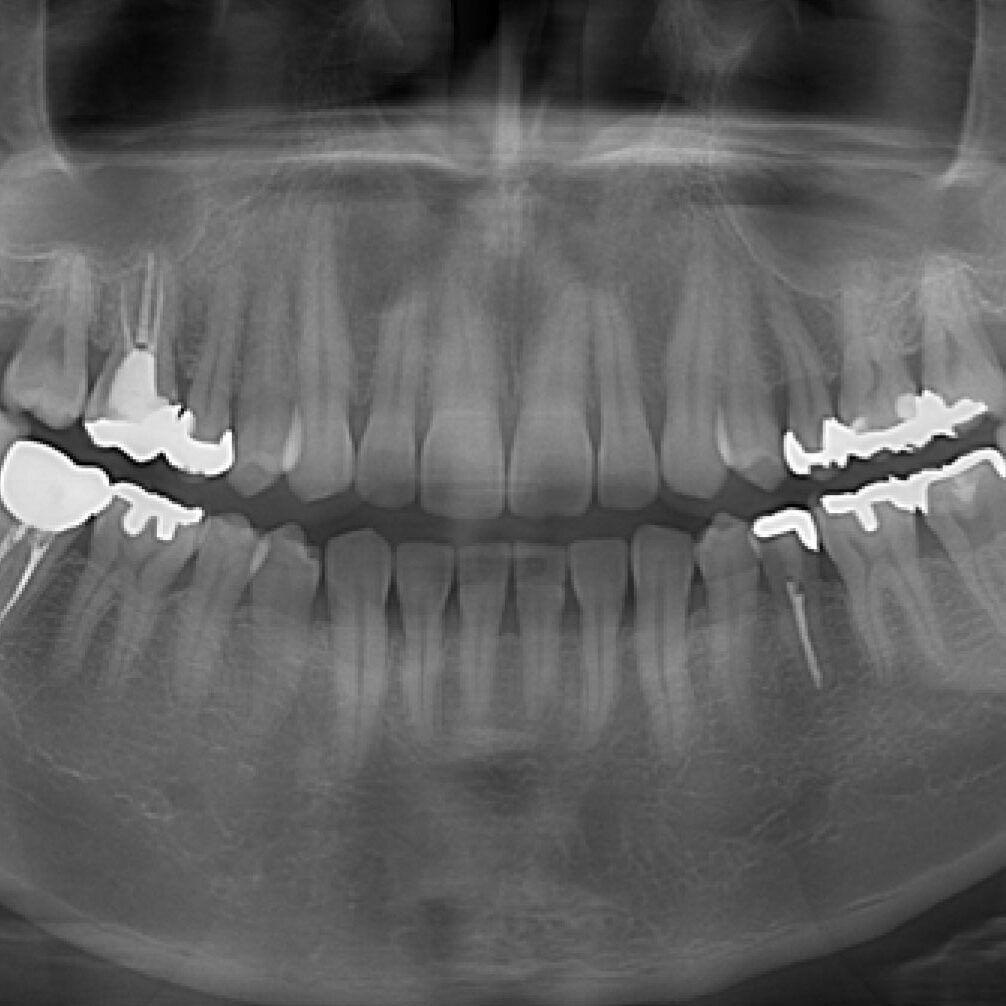
An Orthopantomogram (OPG) and a dental cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scan are both imaging techniques used in dentistry to obtain detailed images of the oral and maxillofacial regions. Here’s a comparison between a conventional OPG scan and a dental CT (cone beam CT or CBCT) scan:
Conventional OPG (Orthopantomogram) Scan:
- Technology:
- 2D Imaging: OPG is a two-dimensional imaging technique that provides a panoramic view of the entire mouth, jaws, and teeth.
- Field of View:
- Large Field of View: OPG captures a wide panoramic image that includes both upper and lower jaws, teeth, temporomandibular joints (TMJ), and surrounding structures.
- Applications:
- General Overview: OPG is commonly used for routine dental examinations and assessments, providing a broad overview of the dental and skeletal structures.
- Orthodontic Planning: It is used in orthodontic treatment planning to evaluate the position of teeth, eruption patterns, and the relationship between the upper and lower jaws.
- Extraction Planning: OPG is useful for planning tooth extractions, especially when assessing the proximity of adjacent structures.
- Radiation Exposure:
- Low Radiation Dose: OPG typically involves a lower radiation dose compared to dental CT scans.
Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Scan:
- Technology:
- 3D Imaging: CBCT is a three-dimensional imaging technique that provides detailed cross-sectional images of the dental and maxillofacial structures.
- Field of View:
- Variable Field of View: CBCT allows for flexibility in choosing the field of view, which can be adjusted based on the specific diagnostic needs of the patient.
- Applications:
- Implant Planning: CBCT is widely used for precise planning of dental implant placement. It provides detailed information about bone density, dimensions, and adjacent structures.
- Endodontic Assessment: CBCT is valuable for assessing root canal anatomy, identifying anomalies, and aiding in complex endodontic cases.
- TMJ Evaluation: CBCT can provide detailed images for evaluating the temporomandibular joints and assessing conditions like temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD).
- Orthognathic Surgery Planning: CBCT is used in the planning of orthognathic surgeries to correct jaw abnormalities.
- Radiation Exposure:
- Higher Radiation Dose: CBCT involves a higher radiation dose compared to a single OPG, but advancements in technology aim to reduce radiation exposure.
Considerations:
- Purpose and Specificity: The choice between OPG and CBCT depends on the specific diagnostic needs of the patient. OPG provides a general overview, while CBCT offers more detailed information for specific applications.
- Radiation Safety: CBCT exposes the patient to a higher radiation dose, so its use is typically justified based on the specific diagnostic requirements.
- Cost: CBCT scans are generally more expensive than OPG, and the choice may be influenced by factors such as cost and insurance coverage.
In summary, OPG and CBCT serve different purposes in dentistry. OPG is a panoramic, two-dimensional imaging technique used for general assessments, while CBCT is a three-dimensional imaging technique that provides detailed information for specific diagnostic and treatment planning purposes. The choice between them depends on the clinical context and the information needed for effective dental care.